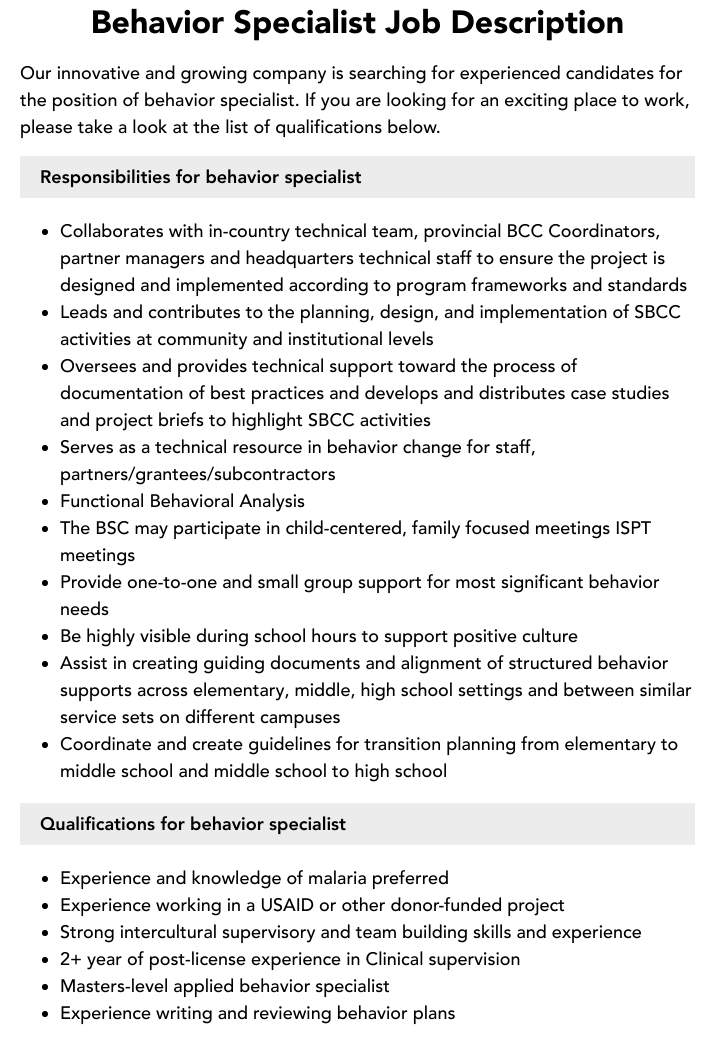
The demand for behavior coaches in the USA has surged over the years as educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and private practice organizations recognize the importance of behavioral health. A behavior coach plays a vital role in helping individuals achieve personal and academic success by guiding them through behavioral changes that enhance their overall well-being.
What is a Behavior Coach?
A behavior coach is a trained professional who specializes in helping clients modify their behaviors. They work with children, adolescents, and adults to develop skills that lead to improved emotional health, better relationships, and enhanced life skills. Behavior coaches may operate independently or within settings such as schools, community centers, or healthcare facilities.
Primary Responsibilities of a Behavior Coach
Behavior coaches perform a variety of tasks aimed at improving a client’s behavioral patterns. Here are the fundamental responsibilities associated with this role:
1. Conducting Assessments
Behavior coaches start by conducting comprehensive assessments to understand a client’s specific issues, strengths, and weaknesses. These assessments may include interviews, questionnaires, and observation.
2. Developing Customized Plans
Based on the assessment results, a behavior coach formulates individualized plans tailored to the client’s needs. These plans typically outline specific goals, strategies, and expected outcomes.
3. Implementing Interventions
Behavior coaches utilize various interventions such as positive reinforcement, structured environments, and cognitive-behavioral strategies to facilitate change.
4. Monitoring Progress
Regularly tracking progress is crucial in behavior coaching. Coaches evaluate the effectiveness of strategies and adjust plans as necessary to optimize outcomes.

5. Collaborating with Other Professionals
Behavior coaches often work alongside psychologists, teachers, and social workers to ensure a cohesive approach to the client’s developmental needs.
Skills Required for Behavior Coaches
Successful behavior coaches possess a blend of interpersonal, analytical, and organizational skills. Here are some essential skills necessary for this role:

1. Strong Communication Skills
Effective verbal and written communication is crucial for behavior coaches to articulate plans and provide feedback to clients and their families.
2. Empathy and Compassion
Understanding a client’s emotional state and demonstrating genuine concern fosters a trusting relationship, which is fundamental for facilitating change.

3. Problem-Solving Abilities
Behavior coaches must identify and address obstacles that hinder a client’s progress, employing creativity and critical thinking in their approach.
4. Knowledge of Behavioral Theories
Proficiency in behavioral theories and techniques allows coaches to apply appropriate methods effectively.
Tools and Technologies Used in Behavior Coaching
Advancements in technology have provided behavior coaches with various tools to enhance their practices. Here are some of the most widely used:
1. Behavioral Tracking Software
Software such as BetterBehaviors enables coaches to monitor client behavior over time, providing valuable data to inform interventions.
2. Virtual Coaching Platforms
Platforms like Coaching.com allow coaches to connect with clients remotely, expanding their reach and providing support regardless of location.
3. Assessment Tools
Standardized assessment tools, such as the Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC), help behavior coaches gather critical data on client behavior and emotional health.
4. Mobile Applications
Apps designed for behavior tracking and mindfulness can enhance client engagement and encourage self-monitoring between sessions.
Education and Certification for Behavior Coaches
To become a successful behavior coach, individuals typically require specific educational backgrounds and certifications.
1. Relevant Educational Background
A bachelor’s degree in psychology, social work, education, or a related field is often considered the minimum requirement. Many behavior coaches pursue further education, such as a master’s degree or specialized training in behavior analysis.
2. Professional Certifications
Obtaining certifications can enhance credibility and provide a competitive edge. Notable certifications include:
- Certified Behavior Analyst (CBA)
- Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA)
- National Certified Counselor (NCC)
Pros and Cons of Behavior Coaching
Like any profession, behavior coaching comes with its unique advantages and challenges. Here’s a brief overview:
Pros
- Opportunity to make a significant positive impact on clients’ lives.
- Flexible work environments, including remote coaching possibilities.
- High demand for services leads to job security.
- Diverse clientele offers a dynamic work experience.
Cons
- Emotional toll from working with clients facing serious challenges.
- Potential for burnout due to case loads and emotional demands.
- Income can vary significantly based on clientele and location.
- Constant need for professional development and training to stay updated.
Comparison Table of Popular Coaching Platforms
| Platform | Features | Price | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| BetterBehaviors | Behavior tracking, reporting, client management | $40/month | Behavior analysts and coaches |
| Coaching.com | Video conferencing, scheduling, resources | $29/month | General coaching practices |
| Teachable | Online course creation, student management | $39/month | Coaches offering structured programs |
Tips for Aspiring Behavior Coaches
If you’re considering a career as a behavior coach, here are some practical tips to help you on your journey:
1. Pursue Relevant Education
Investing time in acquiring the right educational background is essential. Aim for degrees and coursework that offer insights into psychological theories and behavioral modifications.
2. Gain Practical Experience
Seek internships, volunteer work, or entry-level positions in related fields. This hands-on experience will enhance your understanding and ability to connect with clients.
3. Network with Professionals
Joining professional organizations, attending conferences, and connecting on platforms like LinkedIn can open doors to valuable opportunities and mentorship.
4. Stay Updated on Trends
Continuous learning is key. Subscribe to industry journals, attend workshops, and participate in webinars to keep abreast of new techniques and research findings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What qualifications do I need to become a behavior coach?
Typically, a bachelor’s degree in psychology or a related field is required. Further certification, such as BCBA, can enhance job prospects.
Can behavior coaches work independently?
Yes, many behavior coaches run their own private practices, offering flexible services tailored to individual clients’ needs.
What types of clients do behavior coaches work with?
Behavior coaches work with a wide range of clients, including children with behavioral issues, students, adults seeking personal development, and individuals coping with mental health challenges.
How much do behavior coaches earn?
Salary can vary significantly based on location, experience, and setting. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for health educators, which includes behavior coaches, was around $61,000 as of 2022.
Conclusion
In summary, the role of a behavior coach is multifaceted and rewarding. By understanding the job description, necessary skills, tools, and strategies for success, you can embark on a fulfilling career that positively impacts individuals and communities. As interest in behavioral health continues to grow, so does the importance of trained professionals in this vital field.