In today’s rapidly evolving educational landscape, the role of an instructional coach in elementary schools has gained significant importance. Instructional coaches serve as vital resources for teachers, helping to enhance instructional practices, improve student engagement, and foster a culture of continuous learning. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various aspects of instructional coaching, including its definition, strategies, and the platforms and technologies that support effective coaching.
What is an Instructional Coach?
An instructional coach is a trained professional who collaborates with teachers to improve their instructional methods and practices. This role is integral to fostering a supportive environment where teachers can experiment, receive feedback, and grow in their teaching abilities. Instructional coaches provide personalized support tailored to the unique needs of teachers and students.
Historical Context
The practice of instructional coaching emerged in the late 20th century as schools recognized the need for ongoing professional development. Unlike traditional models of professional development that may involve one-time workshops, instructional coaching emphasizes continuous support, collaboration, and in-classroom application.

The Importance of Instructional Coaching in Elementary Education
Instructional coaching plays a crucial role in enhancing educational outcomes. Here are several reasons why instructional coaching is vital in elementary education:
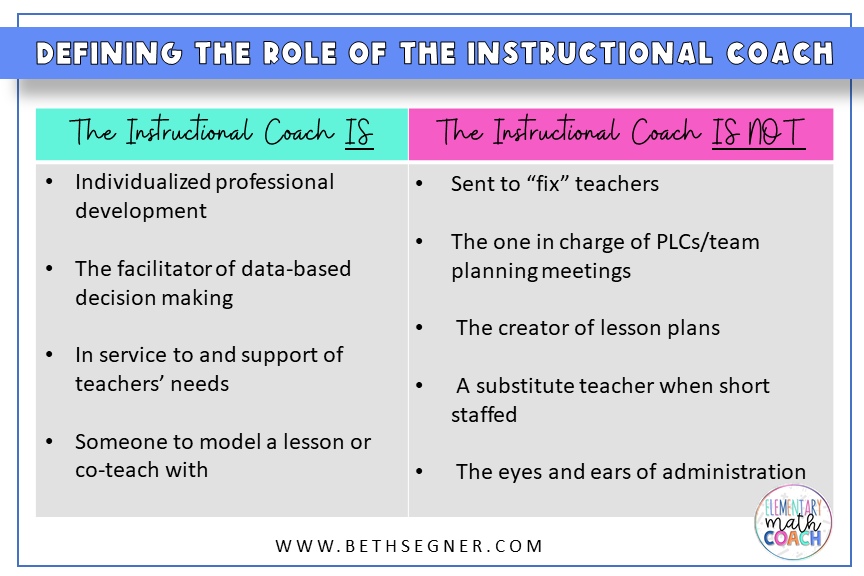
- Personalized Support: Coaches work closely with teachers to identify specific areas for improvement, ensuring that support is relevant and impactful.
- Improved Teacher Effectiveness: Through observations and feedback, coaches help teachers refine their techniques, leading to improved classroom performance.
- Enhanced Student Learning: As teachers improve their practice, students benefit from more effective instruction, which can boost academic achievement.
- Building a Positive School Culture: Coaches foster collaboration and professional dialogue among teachers, contributing to a supportive educational environment.
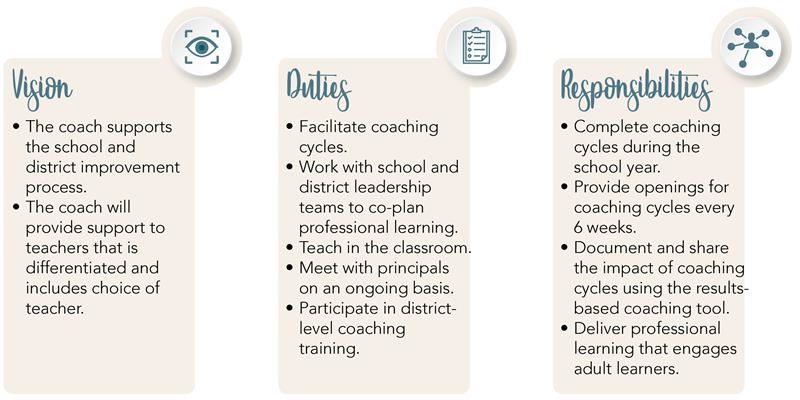
Key Responsibilities of an Instructional Coach
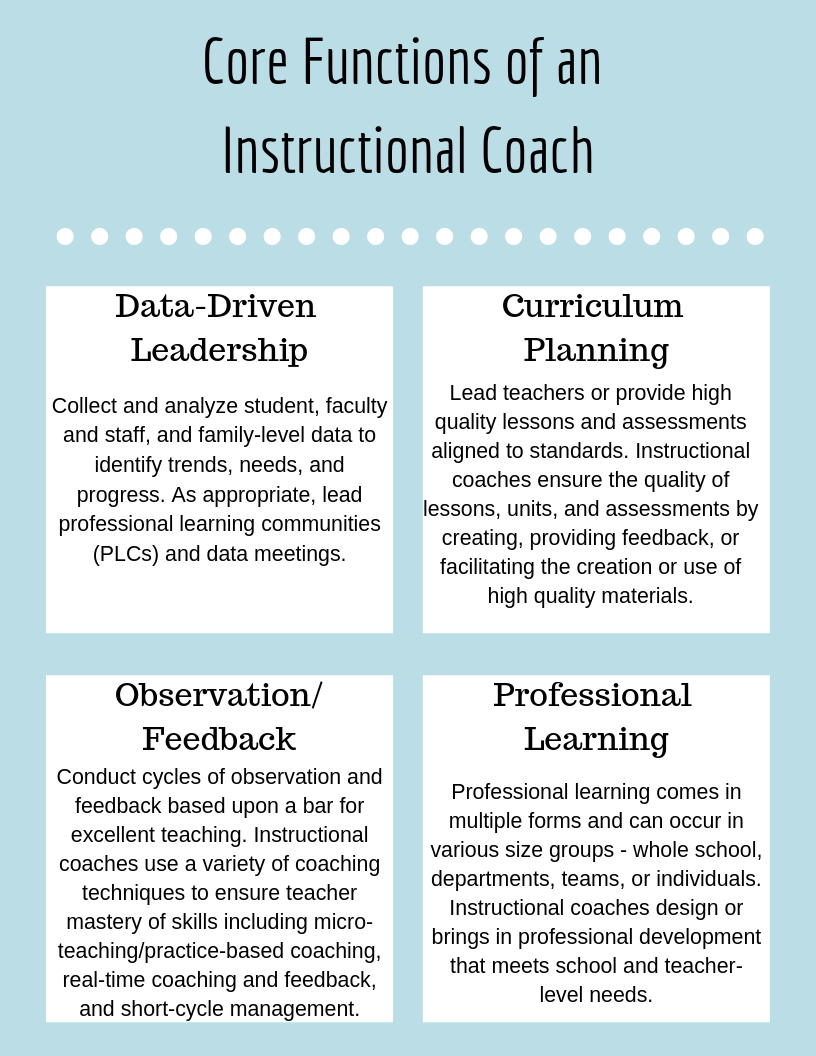
The role of an instructional coach encompasses a variety of responsibilities, including:
1. Conducting Observations
Coaches regularly observe classroom instruction to provide constructive feedback and support.

2. Designing Professional Development
Coaches create tailored professional development plans that address the specific needs of teachers and their students.
3. Collaborating with Teachers
Working alongside teachers, coaches facilitate discussions on instructional strategies, lesson planning, and student assessment.
4. Implementing New Curricular Strategies
Coaches introduce new teaching methodologies and technologies to enhance instructional practices.
5. Data Analysis
Instructional coaches help teachers analyze student performance data to inform instructional decisions.

Strategies Used by Instructional Coaches
Instructional coaches employ various strategies to support teachers effectively. Here are some popular approaches:

1. Co-Teaching
In co-teaching, the coach collaborates with the teacher in the classroom, modeling instructional techniques while actively engaging with students. This approach allows teachers to observe effective practices in real-time.
2. Peer Coaching
Facilitating peer-to-peer coaching can empower teachers to learn from one another, fostering a culture of collaboration and shared expertise.
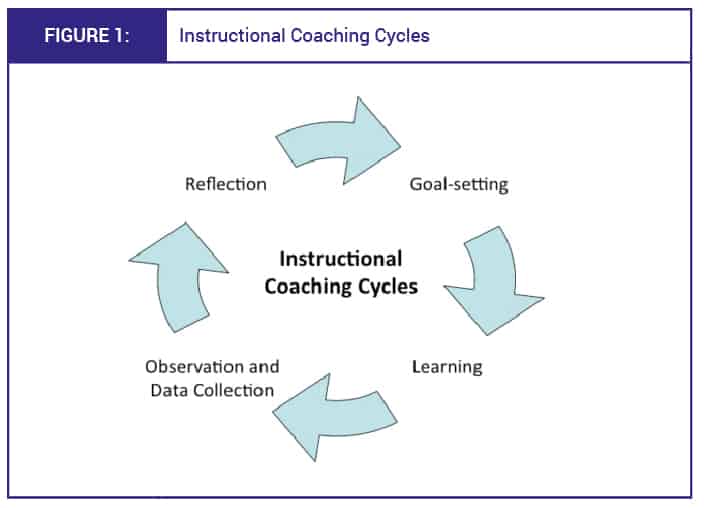
3. Workshops and Training
Organizing workshops focused on specific teaching strategies or technologies can provide teachers with the knowledge and skills necessary for improvement.
4. One-on-One Coaching
Individualized sessions allow coaches to address teachers’ unique challenges, providing personalized feedback and support.

Platforms and Technologies Supporting Instructional Coaching
Several platforms and technologies have emerged to support instructional coaches in their roles. Below is a table highlighting some of these tools:
| Platform/Technology | Purpose | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edthena | Video observation and feedback | Easy to use, promotes reflective practice | Requires tech proficiency |
| Coaching Platform | Goal setting and tracking | Customizable, user-friendly | May lack comprehensive features |
| GoReact | Video feedback and assessments | Instant feedback, supports remote coaching | Limited student interaction |
Benefits of Instructional Coaching
Instructional coaching offers numerous benefits, both for teachers and students:
1. Professional Growth for Teachers
Through ongoing feedback and support, teachers experience continuous growth, enhancing their teaching practices.
2. Increased Student Engagement
With improved teaching methods, students are more likely to engage actively in their learning.
3. Building a Supportive Network
Coaches help cultivate stronger relationships among faculty, promoting a collaborative atmosphere.
4. Data-Driven Instruction
Through data analysis, coaches guide teachers in making informed instructional decisions that benefit student learning.
Challenges Faced by Instructional Coaches
Despite the many advantages, instructional coaches may encounter challenges:
1. Resistance to Change
Some teachers may be resistant to new strategies or feedback, making it difficult for coaches to implement change effectively.
2. Time Constraints
Balancing coaching duties with administrative responsibilities can limit the time available for meaningful interactions.
3. Variability in Teacher Readiness
Coaches may face disparities in teachers’ willingness or ability to adapt to new practices, requiring tailored approaches to meet diverse needs.
Tips for Effective Instructional Coaching
To maximize the impact of instructional coaching, consider the following tips:
- Establish Trust: Build rapport with teachers to create a safe environment for sharing and feedback.
- Be Flexible: Adapt coaching strategies to align with the individual needs and preferences of teachers.
- Encourage Reflection: Promote self-reflection among teachers to foster a growth mindset.
- Use Data Wisely: Leverage student performance data to inform coaching discussions and decisions.
Comparative Analysis of Coaching Models
Different instructional coaching models exist, each with its unique approach to supporting teachers. Below is a comparison of two popular models:
| Coaching Model | Overview | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content-Focused Coaching | Emphasizes subject-specific strategies and practices | Deepens content knowledge, tailored support | May overlook broader instructional practices |
| Process-Oriented Coaching | Focuses on general instructional strategies and teacher development | Encourages holistic growth, adaptable across subjects | Less emphasis on content-specific strategies |
Conclusion
Instructional coaches are an invaluable asset to elementary schools, providing essential support to teachers and contributing to improved student outcomes. By fostering a culture of collaboration, encouraging professional growth, and utilizing innovative strategies and technologies, instructional coaches play a critical role in shaping the future of education. As schools continue to embrace instructional coaching, it is essential to understand and appreciate the significant impact these professionals have in transforming teaching and learning in elementary education.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What qualifications do instructional coaches need?
While specific qualifications can vary by district, most instructional coaches hold advanced degrees in education and have extensive teaching experience.
How can schools effectively implement an instructional coaching program?
Successful implementation involves clear communication of goals, providing adequate training for coaches, and fostering a culture of trust and collaboration among faculty.
What is the difference between instructional coaching and mentoring?
While both focus on teacher development, instructional coaching is typically more data-driven and tailored to improve instructional practices, whereas mentoring may emphasize general support and guidance.
How can technology enhance the role of instructional coaches?
Technology can facilitate data analysis, enable video observations for feedback, and streamline communication and collaboration among coaches and teachers.
For further insights on instructional coaching, consider exploring resources from the Education Corner and the Teaching Channel.