In the dynamic world of education, the role of a teaching coach has become pivotal in enhancing instructional quality and fostering professional development among educators. Teaching coaches are more than just mentors; they are collaborators who assist teachers in improving their methodologies for the benefit of their students. This article delves into the multifaceted role of a teaching coach, providing insights into effective strategies, cultural nuances, and practical tips to excel in this role.
The Importance of Teaching Coaches
Teaching coaches play a crucial role in the educational landscape, particularly in the United States, where diverse teaching methods and student needs present unique challenges. Their importance can be highlighted through several factors:
- Enhancing Teacher Effectiveness: Coaching fosters continuous professional growth.
- Improving Student Outcomes: Effective teaching translates to better learning experiences.
- Building a Collaborative Culture: Coaches promote teamwork and shared goals among educators.
Understanding the Role of a Teaching Coach

Key Responsibilities of a Teaching Coach
A teaching coach wears many hats. Here are some of the key responsibilities:

- Observe classroom instruction and provide constructive feedback.
- Facilitate professional development workshops.
- Assist in curriculum development and implementation.
- Support teachers in reflecting on their practices.
- Act as an intermediary between teachers and administration.
Qualities of a Successful Teaching Coach

A successful teaching coach embodies several key qualities that contribute to their effectiveness:
- Empathy: Understanding the challenges teachers face fosters trust.
- Communication Skills: Clear, open dialogue is essential for effective coaching.
- Expertise: Deep knowledge of pedagogy and subject matter.
- Flexibility: Adapting strategies to meet individual teacher needs.
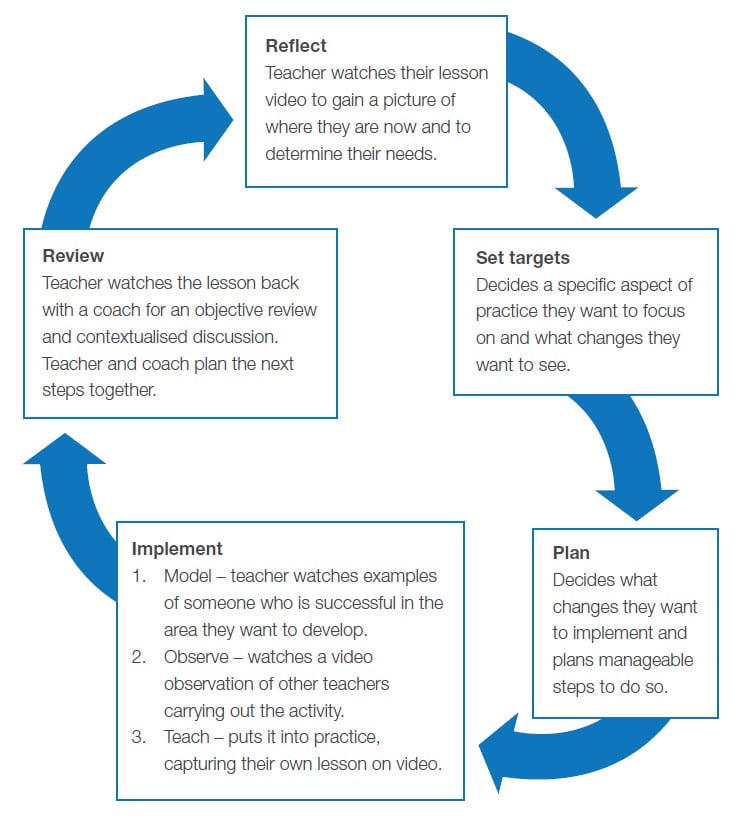
Strategies to Become an Effective Teaching Coach
1. Build Trusting Relationships

Trust is the foundation of a successful coaching relationship. Establishing a rapport with teachers fosters open communication and a willingness to embrace feedback. Here are ways to build trust:
- Be approachable and supportive.
- Practice active listening to understand teachers’ concerns.
- Respect confidentiality in discussions.
2. Utilize a Data-Driven Approach
Using data effectively can significantly enhance coaching strategies. Collecting and analyzing student performance data helps identify areas for improvement. Here’s how to integrate data into coaching:
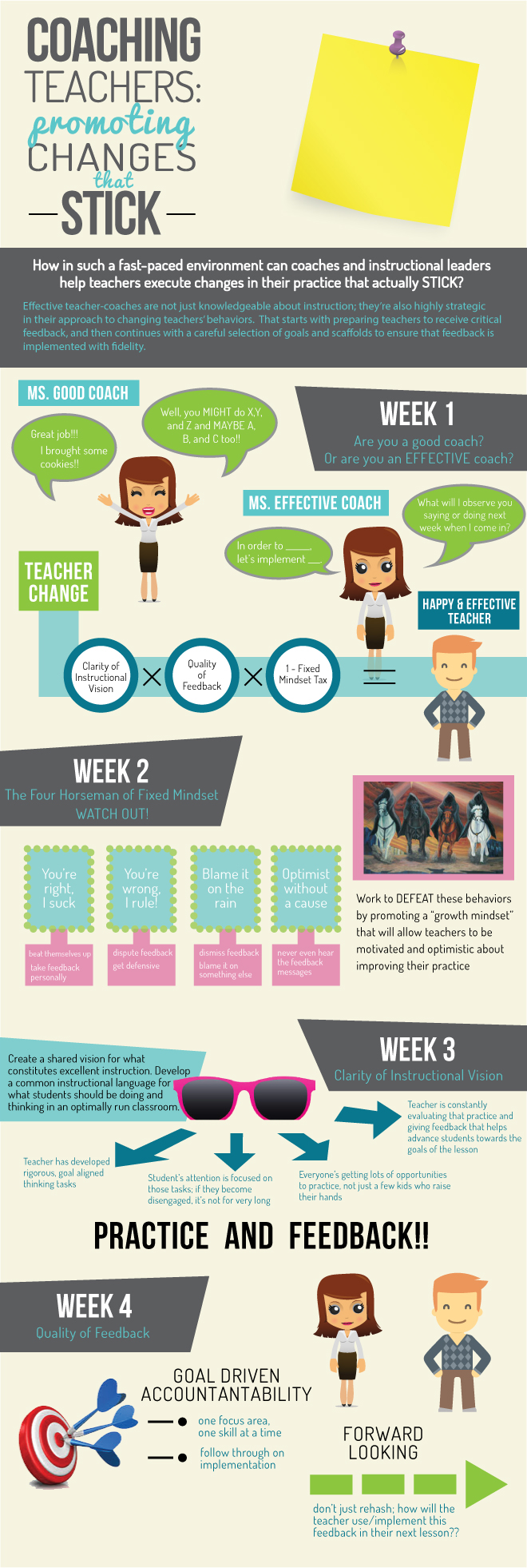
- Set measurable goals based on data analysis.
- Regularly review progress with teachers.
- Adjust strategies based on data insights.
3. Foster Collaborative Learning
Encouraging teamwork among teachers can lead to shared learning experiences and collective problem-solving. Consider these practices:
- Organize team teaching opportunities.
- Facilitate peer observation sessions.
- Encourage participation in professional learning communities.
4. Provide Continuous Feedback
Regular feedback is vital for teacher growth. Here’s how to make feedback effective:
- Be specific and focused on observable behaviors.
- Use video recordings for self-reflection.
- Encourage self-assessment alongside feedback.
5. Embrace Professional Development
A great coach is also a lifelong learner. Stay updated with the latest teaching strategies and educational research. Options for professional development include:
- Attending workshops and seminars.
- Participating in online courses.
- Keeping abreast of current educational literature.
6. Celebrate Success
Recognizing achievements, no matter how small, can motivate teachers and reinforce positive changes. Consider these methods of celebration:
- Public recognition during staff meetings.
- Creating a “success wall” in the staff lounge.
- Sending out newsletters highlighting accomplishments.
7. Leverage Technology
In a technology-driven world, incorporating digital tools can streamline coaching. Tools to consider include:
| Tool | Purpose | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Classroom | Classroom management and communication | Easy to use; integrates with G Suite | Can be overwhelming for less tech-savvy teachers |
| Zoom | Virtual coaching sessions | Flexible and accessible; allows for recorded sessions | Requires reliable internet; may face technical issues |
| Edmodo | Collaborative learning community | User-friendly; promotes collaboration | Limited features in the free version |
Pros and Cons of Being a Teaching Coach
While being a teaching coach is rewarding, there are both advantages and challenges. Understanding these can help prepare for the role:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Opportunity to impact teacher development | Possible resistance from some teachers |
| Access to continuous learning and professional growth | Time-consuming, balancing multiple responsibilities |
| Development of strong professional relationships | Emotional labor involved in supporting peers |
Cultural Context of Teaching Coaching in the USA
The role of a teaching coach can vary significantly based on cultural and regional contexts within the United States. Understanding these nuances is essential for effective coaching.
Regional Variations
Different regions in the USA may have distinct educational priorities and challenges. Key observations include:
- In urban areas, coaches may focus on addressing diverse student needs.
- Rural regions may prioritize classroom management and resourcefulness due to limited access to educational materials.
- Suburban areas may emphasize standardized test preparation and advanced instructional techniques.
Diversity and Inclusion
Coaching in a multicultural environment necessitates a focus on inclusion and equity. Here are ways to address these issues:
- Promote culturally responsive teaching strategies.
- Incorporate student voices in the coaching process.
- Provide resources for addressing biases in the classroom.
FAQs About Being a Teaching Coach
What qualifications do I need to become a teaching coach?
Most teaching coaches have at least a bachelor’s degree in education, with many holding advanced degrees or certifications in instructional leadership.
How can I measure my effectiveness as a teaching coach?
Effectiveness can be gauged through teacher feedback, student performance data, and the overall improvement in instructional strategies within the classroom.
Can teaching coaches work part-time?
Yes, some coaches work part-time or in hybrid roles, combining coaching with teaching responsibilities, though this can affect the depth of their coaching relationships.
What are some common challenges faced by teaching coaches?
Common challenges include resistance to feedback, time constraints, and balancing administrative duties with coaching responsibilities.
How can technology enhance coaching practices?
Technology can streamline communication, provide access to resources, facilitate virtual coaching sessions, and support data analysis for performance tracking.
Conclusion
Becoming a good teaching coach is a rewarding venture that requires dedication, adaptability, and a passion for education. By employing effective strategies, fostering positive relationships, and staying attuned to the cultural context of teaching, coaches can significantly impact both teachers and students. The journey may have its challenges, but the rewards—transforming educational practices and contributing to student success—are unparalleled.
For further reading and resources on educational coaching, consider exploring the following links: