Purdue University, located in West Lafayette, Indiana, has a storied tradition in college football. As a member of the Big Ten Conference, Purdue competes at the highest level of NCAA football, making the role of head coach a significant one. Understanding the salary of Purdue football coaches sheds light on the broader financial landscape of college sports and the factors that influence coaching salaries.
Understanding Coaching Salaries in College Football
Coaching salaries in college football can vary widely based on several factors, including the school’s revenue, success of the program, and historical precedence. Purdue’s football coach salary structure is no different. In this section, we will explore what factors contribute to the salaries of college football coaches.
Revenue Generation
The primary driver of a football coach’s salary at Purdue is the revenue generated by the football program.
Ticket Sales
Game day attendance directly correlates with ticket sales, which form a significant portion of the athletic department’s revenue. Purdue’s Ross–Ade Stadium has a seating capacity of approximately 57,236, and full attendance can lead to substantial income.
Television Contracts
Television deals are another major source of income. The Big Ten Conference has lucrative contracts with networks like ESPN and Fox, significantly boosting the financial resources available for Purdue’s athletic programs.
Merchandising and Sponsorships
Purdue’s branding and the popularity of its football team benefit from merchandising and sponsorship deals, which help fund coaching salaries.
Historical Performance
The success of the program over the years also impacts salary levels. Coaches who lead teams to victory and bowl games tend to see financial rewards, as success boosts fan engagement and program visibility.
Comparative Analysis
Examining the salaries of coaches at comparable schools in the Big Ten provides insight into how Purdue’s salaries stack up. Below is a comparison table of the head coach salaries from various Big Ten schools:
| University | Head Coach Name | Annual Salary |
|---|---|---|
| Purdue University | Ryan Walters | $2.5 million |
| University of Michigan | Jim Harbaugh | $4.5 million |
| Ohio State University | Ryan Day | $4.3 million |
| University of Iowa | Kirk Ferentz | $4.2 million |
| Penn State University | James Franklin | $3.9 million |
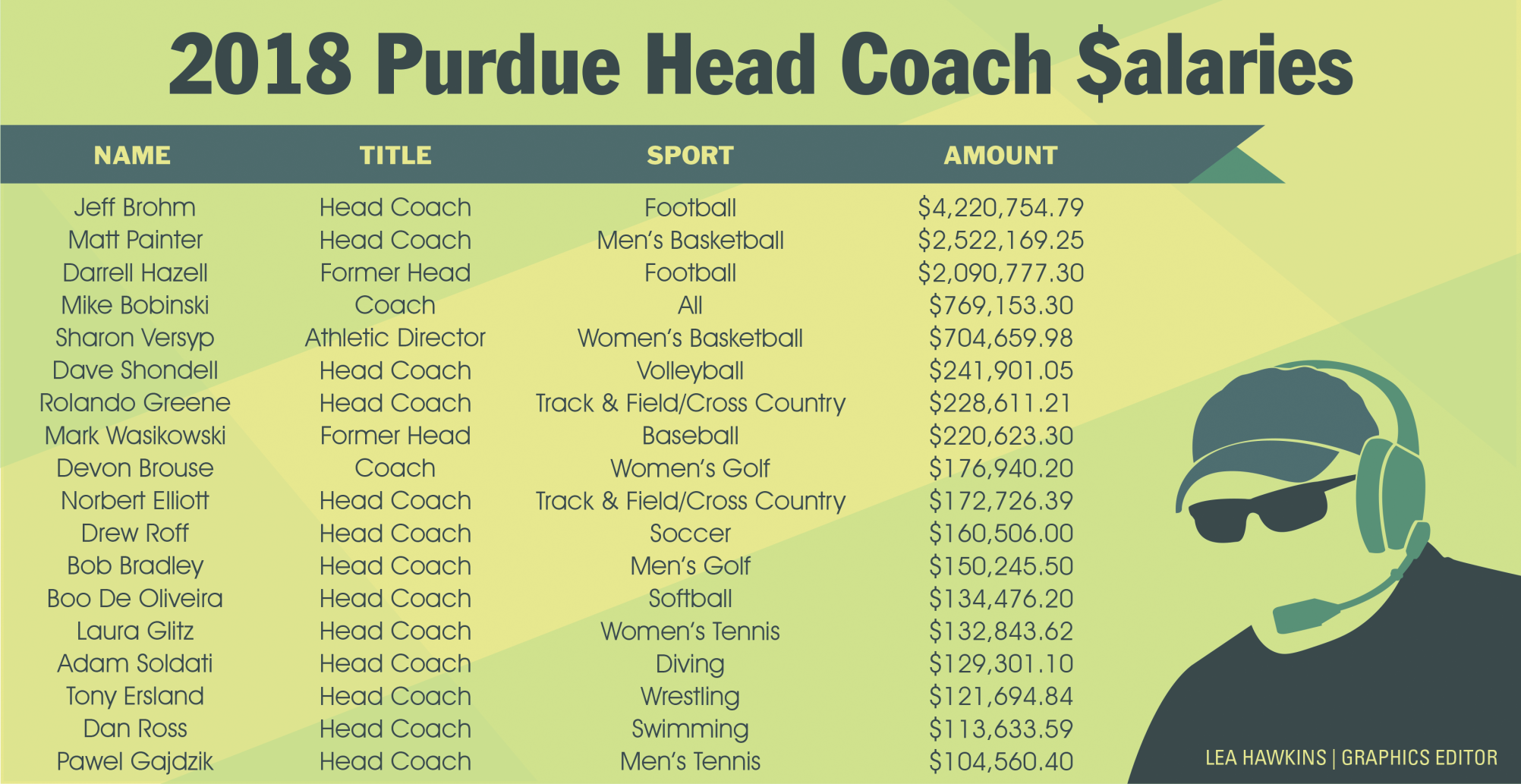
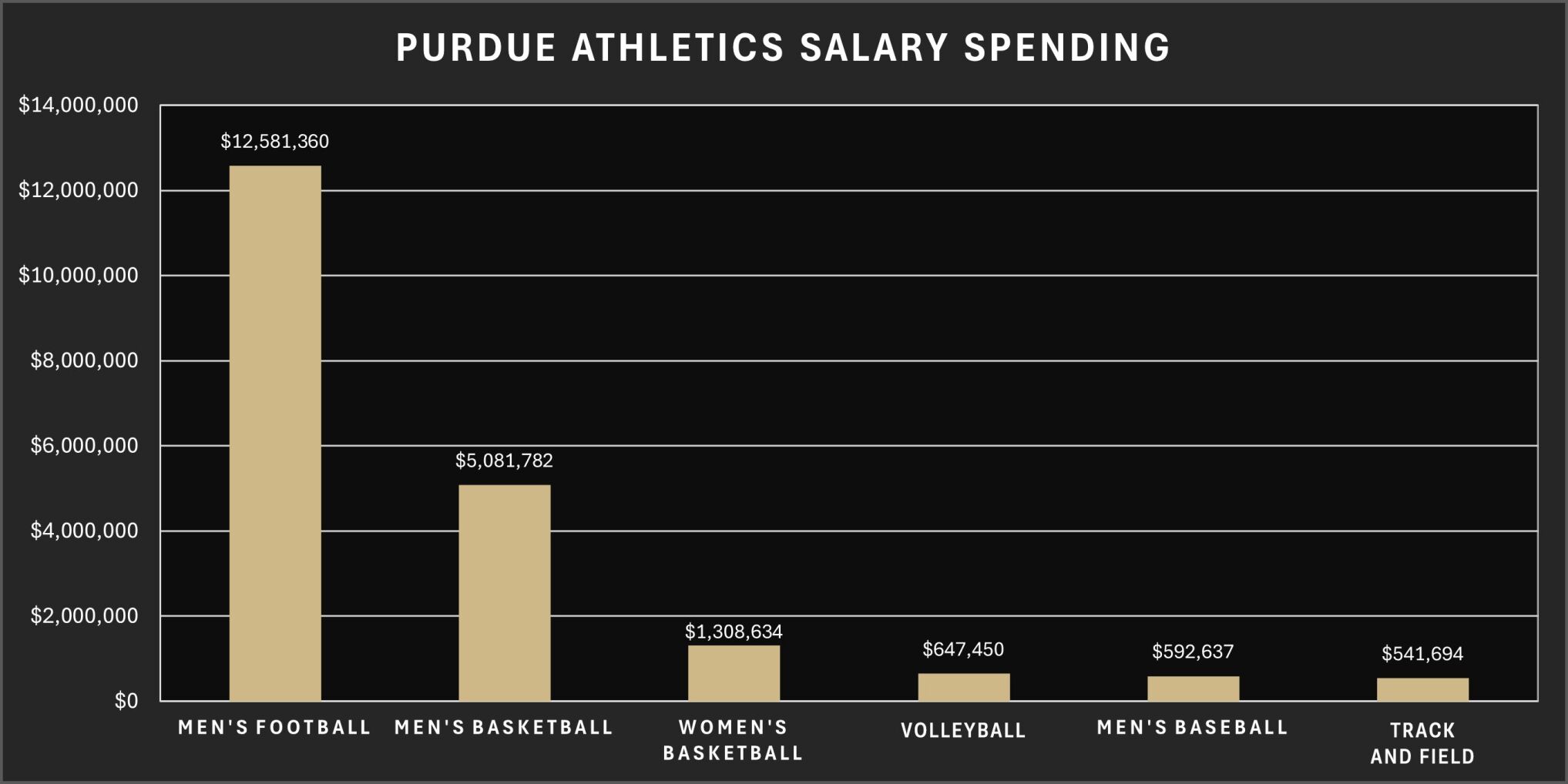
Purdue Football Coach Salary Breakdown
As of 2023, the salary of Purdue’s head football coach, Ryan Walters, is reported to be around $2.5 million annually. This figure may include various incentives based on team performance, attendance, and bowl game appearances.
Base Salary vs. Incentives
Most coaching contracts typically include a base salary plus performance incentives that can significantly increase total earnings. Below are common incentive structures:
- Win Bonuses: Coaches may receive additional bonuses for each win during the season.
- Bowl Game Participation: Financial rewards are common for coaches whose teams qualify for bowl games.
- Recruiting Success: Incentives can sometimes be earned based on recruiting classes’ rankings.
Comparison with Other Major Programs
Purdue’s coaching salary is competitive within the Big Ten, but it is essential to consider the differences in program prestige and success. While Purdue pays $2.5 million, other major programs exceed this figure considerably.

Pros and Cons of Purdue’s Coaching Salary
Pros
- Attracts Talent: Competitive salary helps attract skilled coaches.
- Potential for Growth: With performance, salaries can increase significantly.
- Supportive Environment: Purdue has a strong alumni and fan base that supports the program.
Cons
- Lower than Peers: Comparatively lower than top programs, which may impact recruitment.
- Performance Pressure: Coaches face immense pressure to win and justify their salary.
- Market Volatility: Salaries can fluctuate based on economic conditions and program success.
Future Trends in Coaching Salaries
As college football continues to evolve, coaching salaries are on the rise. Factors contributing to future salary trends may include:
Increased Revenue from Media Rights
As college athletics become more commercialized, the revenue from media rights continues to grow. This financial influx will likely lead to increased salaries for head coaches across the board.
Improved Performance Metrics
Programs are increasingly focusing on data analytics and performance metrics to drive success, potentially leading to higher salaries for successful coaches.
Impact of NIL (Name, Image, and Likeness)
The recent changes around NIL rights allow athletes to profit from their own brand, impacting how schools allocate funds, possibly leading to an increase in coaching salaries to keep pace.
FAQs About Purdue Football Coach Salaries
What is the average salary for college football coaches in the Big Ten?
The average salary for college football coaches in the Big Ten varies, but it generally falls between $2 million and $5 million, depending on the team’s success and historical performance.
How does Purdue’s football program financially support its coaching salaries?
Purdue’s football program supports coaching salaries through ticket sales, donations, sponsorships, and revenue from television contracts.
Are coaching salaries at Purdue expected to increase in the future?
Given the trends in college athletics and potential increases in revenue streams, it is reasonable to expect coaching salaries at Purdue to rise in the coming years.
What are the main factors that influence a football coach’s salary at Purdue?
Main factors include program success, historical performance, revenue generation, and recruiting success.

Conclusion
Purdue’s football coach salary reflects the complex interplay between financial resources, program success, and the wider landscape of college athletics. As Purdue continues to invest in its football program, the expectation is that coaching salaries will grow, attracting top talent to one of Indiana’s premier universities.

Understanding these salaries also invites a broader conversation about the financial implications of college athletics and how they affect not only the programs but also the student-athletes involved.