Instructional coaches play a pivotal role in the educational system, serving as mentors and guides for teachers. Their primary goal is to enhance instructional practices and improve student outcomes. This article delves into the detailed job description of an instructional coach, including roles, responsibilities, required skills, salary expectations, and career outlook, particularly in the USA. We will also provide insights based on cultural and local experiences to help you understand this vital position better.
What is an Instructional Coach?
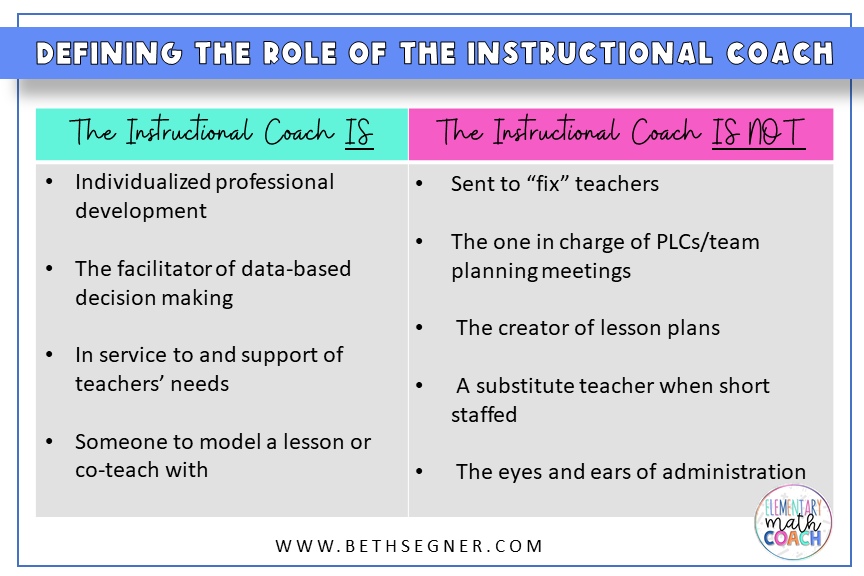
An instructional coach is a professional who collaborates with teachers to enhance their instructional methods, content knowledge, and pedagogical skills. They provide individualized support, facilitate professional development, and promote the implementation of effective teaching strategies within the school environment.
Key Responsibilities of an Instructional Coach
The responsibilities of an instructional coach can vary by district and school, but common duties include:
1. Collaborating with Teachers
Instructional coaches work closely with teachers to assess their instructional practices and identify areas for improvement. This collaboration may involve one-on-one coaching sessions, observation, and modeling lessons.
2. Providing Professional Development
They design and deliver professional development workshops and training sessions aimed at enhancing teaching strategies, integrating technology, and addressing curriculum changes.
3. Analyzing Student Data
Instructional coaches often analyze student performance data to inform instructional decisions, helping teachers adjust their strategies to meet student needs.

4. Supporting Curriculum Implementation
They assist in the implementation of new curricula, ensuring that teachers understand the materials and resources available to them.
5. Promoting Best Practices
Instructional coaches stay abreast of educational research and new teaching methodologies to promote best practices among teaching staff.

Essential Skills and Qualities of an Instructional Coach
Being an effective instructional coach requires a unique blend of skills and personal qualities:
1. Strong Communication Skills
The ability to communicate effectively is crucial for building relationships with teachers and facilitating discussions around instructional practices.

2. Deep Content Knowledge
Instructional coaches must possess a thorough understanding of the subject matter and educational frameworks relevant to their grade level and teaching context.
3. Leadership Skills
As leaders within the educational environment, instructional coaches need to inspire and motivate teachers to embrace change and adopt new methods.

4. Data-Driven Decision Making
Instructional coaches must be adept at analyzing data to drive instructional improvements and effectively support teachers.
Other Important Skills
- Problem-solving abilities
- Adaptability to learn and apply new strategies
- Empathy and understanding towards teacher challenges

Educational Requirements
Generally, instructional coaches hold at least a bachelor’s degree in education or a related field. Many employers also prefer candidates with a master’s degree and a teaching credential or certification. Additional certifications related to instructional coaching and professional development can be beneficial.
Cultural Impact on Instructional Coaching
Cultural context greatly influences the role of instructional coaches in schools across the USA. The approaches they take may vary depending on the community’s unique needs, student demographics, and prevailing educational philosophies.
Local Experiences and Diversity
In diverse urban areas, instructional coaches may focus on culturally responsive teaching practices to better engage students from various backgrounds. Conversely, in rural areas, the emphasis might be on integrating technology to meet students’ needs.
Career Outlook and Salary Expectations
1. Job Outlook
The demand for instructional coaches is growing as schools increasingly recognize the importance of ongoing professional development and teacher support. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects a positive job outlook for educators in general, with positions for instructional coordinators (a related role) expected to grow by 10% from 2020 to 2030.

2. Salary Range
The salary for instructional coaches can vary significantly based on experience, education level, and location. Here’s a breakdown of typical salary ranges:
| Location | Average Salary ($) | Salary Range ($) |
|---|---|---|
| California | 75,000 | 65,000 – 90,000 |
| Texas | 60,000 | 50,000 – 75,000 |
| New York | 80,000 | 70,000 – 95,000 |
| Florida | 55,000 | 45,000 – 70,000 |
Pros and Cons of Being an Instructional Coach
Pros
- Opportunity for professional growth and development.
- Ability to impact teacher effectiveness and student outcomes.
- Engagement with diverse educational strategies and methods.
- Collaboration with passionate educators in a supportive role.
Cons
- Challenges in balancing support with accountability.
- Potential for burnout due to the demanding nature of coaching.
- Difficulty in measuring the direct impact of coaching efforts.
- Need for constant adaptation to new educational standards and practices.
Tips for Aspiring Instructional Coaches
If you are considering a career as an instructional coach, here are some tips to enhance your journey:
- Engage in continuous professional development to keep your skills updated.
- Network with existing instructional coaches to gain insights and advice.
- Seek mentorship opportunities to learn from experienced educators.
- Develop a strong understanding of educational technology and its applications in the classroom.
FAQs About Instructional Coaching
What qualifications do I need to become an instructional coach?
Typically, you need a bachelor’s degree in education, teaching experience, and possibly a master’s degree or additional certifications in instructional coaching.
Is instructional coaching a full-time job?
Yes, instructional coaching is usually a full-time position, although specific roles and responsibilities can vary greatly between schools and districts.
How can an instructional coach help improve student learning?
By working with teachers to refine their teaching strategies, providing relevant professional development, and analyzing student data, instructional coaches directly contribute to improved instructional quality and student learning outcomes.
What distinguishes an instructional coach from a traditional mentor or teacher?
While a mentor might provide advice based on their own experiences, instructional coaches are trained professionals who focus specifically on enhancing teaching practices through systematic coaching and data analysis.
Conclusion
Instructional coaches are essential assets in the education sector, profoundly influencing the quality of teaching and learning. Their unique roles require a diverse skill set, deep knowledge, and a commitment to empowering teachers. With the growing emphasis on educational improvement, the demand for instructional coaches is on the rise. For those passionate about education and teacher support, a career as an instructional coach offers both challenges and rewards.