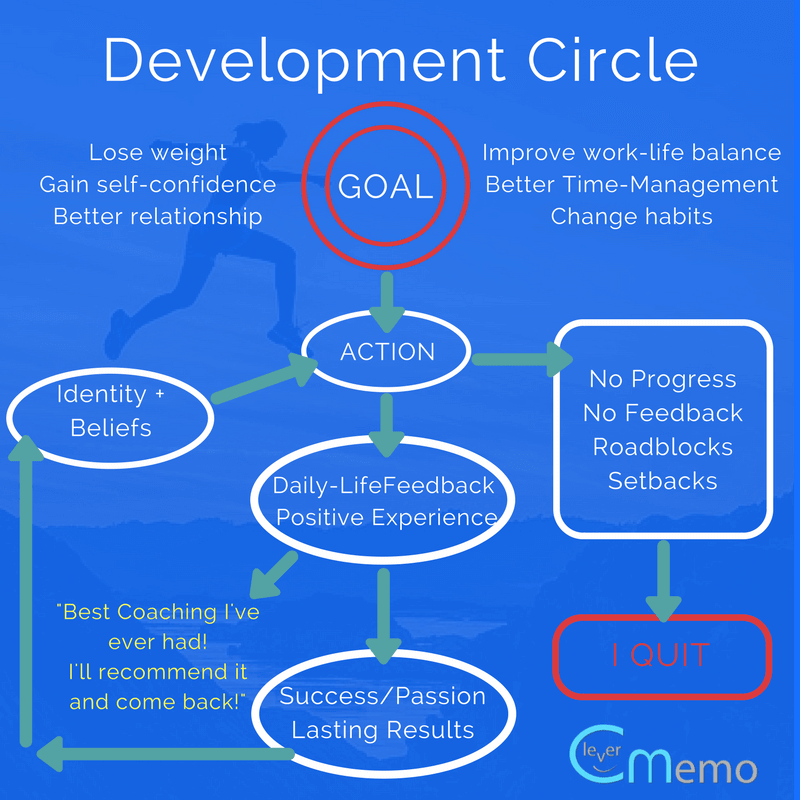
Coaching is more than just a profession; it’s a calling that requires a unique blend of skills, knowledge, and personal attributes that can inspire and transform individuals and teams. Whether you’re coaching youth sports, corporate teams, or personal development clients, knowing how to be a great coach can make all the difference. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the crucial aspects of effective coaching, drawing upon local experiences and insights from various coaching disciplines.
Understanding the Role of a Coach
A coach wears many hats. They are mentors, strategists, motivators, and, at times, confidants. Understanding the multifaceted role of a coach is the first step toward excellence.
Key Responsibilities of a Coach
- Developing skills and strategies
- Providing motivation and encouragement
- Setting goals and benchmarks
- Offering feedback and assessments
- Building team dynamics and culture
Types of Coaching
There are various types of coaching, each with its own unique focus:
- Sports Coaching: Focuses on athletic performance and teamwork.
- Life Coaching: Concentrates on personal development and achieving life goals.
- Executive Coaching: Aims at enhancing leadership skills in a corporate setting.

Comparison Table of Coaching Types
| Coaching Type | Focus Area | Target Audience | Common Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sports Coaching | Athletic performance | Athletes, teams | Drills, simulations |
| Life Coaching | Personal growth | Individuals | Goal setting, accountability |
| Executive Coaching | Leadership skills | Business leaders | Workshops, one-on-one sessions |
Essential Skills for Great Coaching

Communication Skills
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful coaching. A great coach must be able to convey messages clearly, listen actively, and adapt their communication style based on the audience.
Types of Communication Skills
- Verbal Communication: Clear instructions and encouragement.
- Non-verbal Communication: Body language, eye contact, and gestures.
- Written Communication: Emails, feedback forms, and reports.
Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
A great coach understands their clients’ emotions and needs. This emotional intelligence fosters trust and creates strong relationships.
Benefits of Empathy in Coaching
- Builds rapport and trust with clients
- Facilitates open communication
- Enhances motivation and engagement
Adaptability and Flexibility
Not every coaching strategy will work for everyone. A great coach needs to be flexible, adapting their approach based on individual needs and changing circumstances.
Leadership and Motivation
Effective coaching requires strong leadership skills to motivate individuals and teams toward their goals. Great coaches inspire others and create a sense of accountability.

Motivational Techniques
- Positive reinforcement
- Setting achievable goals
- Creating a supportive environment
Building a Coaching Philosophy

Defining Your Vision
Your coaching philosophy should encapsulate your values, beliefs, and approach to coaching. It serves as a foundation for your coaching practice.
Key Elements of a Coaching Philosophy
- Core values (integrity, teamwork, resilience)
- Goals for your clients (skill development, personal growth)
- Approach to coaching (collaborative, directive, empowering)

Developing a Coaching Plan
Assessing Needs and Setting Goals
Understanding your clients’ needs is crucial in developing an effective coaching plan. Conduct assessments and collaborate with clients to set clear, achievable goals.

SMART Goals Framework
Utilize the SMART criteria for goal setting:
- Specific: Clearly define the goal
- Measurable: Set criteria for measuring progress
- Achievable: Ensure the goal is realistic
- Relevant: Align the goal with broader objectives
- Time-bound: Set a deadline for achievement
Creating a Structured Coaching Program
A structured program ensures consistency and progress. Outline sessions, topics, and assessment methods to keep your coaching organized.
Sample Coaching Program Structure
| Session Number | Focus Area | Activities | Assessment Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Goal Setting | Discussion, brainstorming | Self-assessment |
| 2 | Skill Development | Workshops, simulations | Performance metrics |
| 3 | Feedback and Adjustments | One-on-one discussions | Progress reports |
Effective Coaching Techniques
Active Listening
Active listening involves fully engaging with your clients during conversations. This helps to build trust and fosters open communication.
Questioning Techniques
Using the right questions can encourage deeper thinking and reflection. Embrace open-ended questions to facilitate discussion.
Examples of Effective Questions
- What challenges are you currently facing?
- How do you envision your success?
- What obstacles do you believe you need to overcome?
Visualization Techniques
Encourage clients to visualize their goals and successes. This can enhance motivation and provide clarity on their objectives.
Overcoming Common Coaching Challenges
Dealing with Resistance
Resistance can be a significant hurdle in coaching. Understanding the root of this resistance and addressing it constructively is key.
Strategies to Overcome Resistance
- Seek to understand the reasons behind the resistance
- Reframe objections as opportunities for growth
- Engage clients in finding solutions
Handling Difficult Personalities
Every coach will encounter challenging personalities. Establishing clear boundaries and expectations can help manage these situations.
Tips for Managing Difficult Personalities
- Stay calm and composed
- Use assertive communication
- Focus on solutions rather than problems
Measuring Coaching Success
Defining Success Metrics
Success in coaching can be measured in various ways, including goal achievement, personal growth, and improvements in skills.
Common Metrics for Evaluating Coaching Effectiveness
- Client feedback and satisfaction surveys
- Progress reports on set goals
- Self-assessments and reflections
Continuous Improvement and Feedback
Encouraging a culture of feedback and continuous improvement benefits both the coach and the client.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
Importance of Lifelong Learning
Great coaches recognize the value of ongoing education. Staying updated on coaching techniques, tools, and trends is essential for maintaining effectiveness.
Resources for Professional Development
- Coaching certifications (e.g., ICF, EMCC)
- Workshops and seminars
- Books and online courses
Networking with Other Coaches
Building relationships with other coaches can provide valuable insights, support, and opportunities for collaboration.
Conclusion: The Path to Becoming a Great Coach
Becoming a great coach is a journey that requires dedication, empathy, and a commitment to continuous growth. By developing essential skills, refining your coaching philosophy, and employing effective techniques, you can inspire and empower those you coach. Remember, the impact of great coaching extends beyond personal achievements; it fosters teamwork, resilience, and a vibrant community.
FAQs About Becoming a Great Coach
What qualities make a great coach?
A great coach possesses strong communication skills, empathy, adaptability, and the ability to motivate others. They should also have a solid understanding of their specific coaching area.
How can I improve my coaching skills?
Improving coaching skills can be achieved through ongoing education, seeking feedback from clients, and networking with other coaches in your field.
Is it necessary to have formal training to be a coach?
While formal training can be beneficial, many successful coaches come from diverse backgrounds. Personal experience, mentorship, and self-study are also valuable.