Discover the transformative power of the coaching cycle in education. This guide will walk you through essential strategies, real-world applications, and insights into teacher development.
What is the Coaching Cycle?
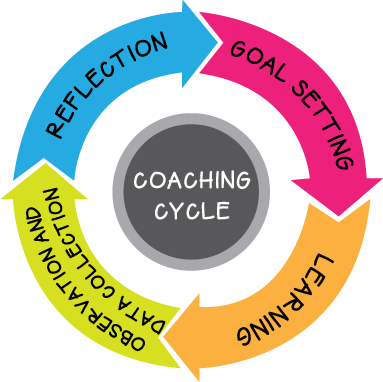
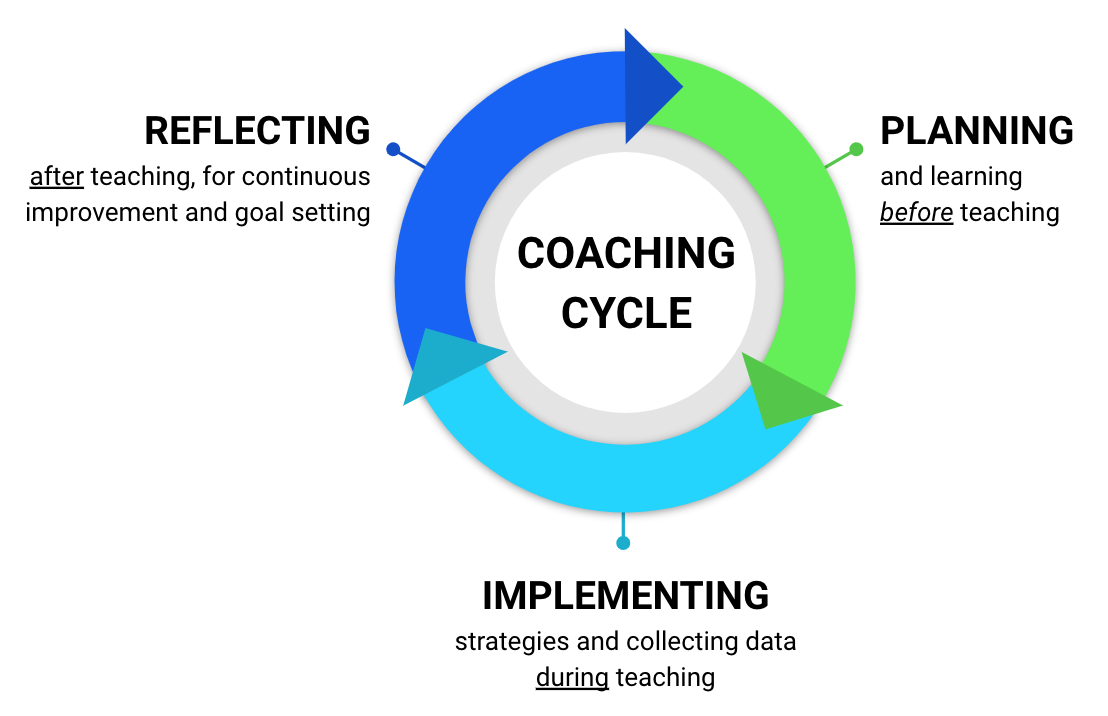
The coaching cycle is a systematic, reflective process aimed at improving teaching practices and student outcomes. Originating from the need to provide tailored support for teachers, the coaching cycle typically encompasses a series of phases: planning, observation, feedback, and reflection. This methodology not only fosters professional growth for educators but also enhances the learning experience for students.
Why is the Coaching Cycle Important?
In the context of American education, the coaching cycle has become increasingly vital due to the demands for accountability and the need for continuous improvement in teaching practices. By engaging in coaching, teachers can:
- Receive personalized support tailored to their individual needs.
- Implement evidence-based practices in the classroom.
- Enhance student engagement and learning outcomes.
- Foster a collaborative culture within the school.
Key Phases of the Coaching Cycle
The coaching cycle is composed of several integral phases, each contributing to the overall effectiveness of the process. Below are the primary phases of the coaching cycle:
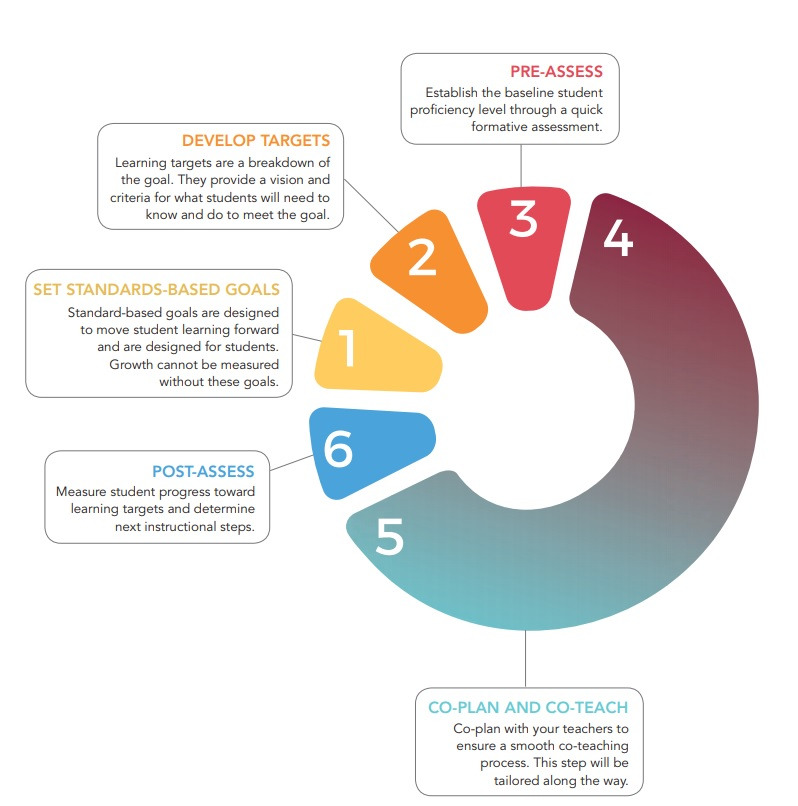
1. Planning
The planning phase involves setting goals based on the teacher’s specific needs and the desired outcomes for students. During this time, the coach and teacher collaborate to develop a targeted action plan.
2. Observation
In the observation phase, the coach observes the teacher in the classroom to gather data on teaching practices. This data can be qualitative or quantitative and is critical for providing constructive feedback.
3. Feedback
Feedback is an essential part of the coaching cycle. The coach shares observations with the teacher, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement. Effective feedback is specific, actionable, and non-evaluative.

4. Reflection
Reflection allows teachers to consider their practices and the feedback received. This meta-cognitive process encourages growth and fosters a mindset of continuous improvement.
Benefits of the Coaching Cycle
Implementing the coaching cycle has numerous benefits for educators, students, and educational institutions alike. Here are some key advantages:
For Teachers
- Enhanced teaching skills through ongoing professional development.
- Increased confidence in implementing new strategies.
- Access to ongoing support and resources.
For Students
- Improved academic performance due to refined teaching methodologies.
- Increased engagement and motivation in learning.
For Schools
- A culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.
- Stronger teacher retention rates through professional support.
The Role of Coaches in the Coaching Cycle
Coaches play a crucial role in the success of the coaching cycle. They are not just evaluators but mentors and facilitators of professional growth. Here’s what makes an effective coach:
Characteristics of Effective Coaches
- Strong communication skills for clear and constructive feedback.
- Empathy and understanding to build trust and rapport.
- A deep understanding of teaching practices and educational theory.
Types of Coaching Models
There are various coaching models that can be utilized within the coaching cycle. Some popular models include:
- Peer Coaching
- Instructional Coaching
- Cognitive Coaching

Comparison Table of Coaching Models
| Coaching Model | Focus | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peer Coaching | Collaborative practice among equals. | Mutual support and shared knowledge. | May require time for building trust. |
| Instructional Coaching | Focus on specific teaching strategies. | Targeted improvement in instruction. | Requires expertise in desired strategies. |
| Cognitive Coaching | Enhancing teacher thinking and reflection. | Empowers teachers to self-assess. | Time-intensive; focuses on deep understanding. |
Tips for Implementing the Coaching Cycle
For Coaches
- Build strong relationships with teachers to encourage openness.
- Set clear, achievable goals for each session.
- Regularly check in on the progress and adjust the approach as needed.
For Teachers
- Be open to feedback and willing to try new strategies.
- Reflect on your practices regularly and document your progress.
- Communicate your needs and challenges with your coach.
Challenges within the Coaching Cycle
While the coaching cycle is beneficial, it does face challenges. Understanding these challenges can help coaches and teachers navigate the process more effectively.
Common Challenges
- Resistance to change from teachers.
- Time constraints within the school schedule.
- Inconsistent implementation across different teams.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
- Foster a growth mindset among staff and encourage risk-taking.
- Schedule dedicated time for coaching sessions.
- Provide ongoing professional development for coaches.
Real-World Applications of the Coaching Cycle in the USA
Many schools across the United States have successfully implemented the coaching cycle. Here are a few examples:
Case Study: New York City Schools
In New York City, several schools have adopted the coaching cycle as part of their professional development program. This initiative focuses on improving literacy instruction through targeted coaching. Teachers receive support in small group settings, allowing for personalized feedback and collaboration.
Case Study: Chicago Public Schools
Chicago Public Schools utilize instructional coaches to enhance the quality of classroom instruction. These coaches work closely with teachers to implement data-driven instruction, helping teachers analyze student performance and adjust their practices accordingly.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the purpose of the coaching cycle for teachers?
The coaching cycle aims to improve teaching practices through a structured process of planning, observation, feedback, and reflection, ultimately enhancing student learning outcomes.
How long does a typical coaching cycle last?
The length of a coaching cycle can vary based on the goals and specific needs of the teachers involved. Typically, a cycle can last from a few weeks to a full academic semester.
Can coaching be effective in virtual classrooms?
Yes, coaching can be effective in virtual classrooms. Coaches can utilize video observations and online feedback tools to support teachers in remote learning environments.
What are the qualifications needed to be an effective coach?
Effective coaches often have a strong background in education, including experience in teaching and a solid understanding of pedagogical practices. Additionally, they should possess strong communication and interpersonal skills.