In today’s rapidly evolving educational landscape, the role of an instructional coach has emerged as a vital component in enhancing teaching practices and improving student outcomes. But what exactly is an instructional coach, and how do they contribute to the educational environment? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of this pivotal role, exploring their responsibilities, effective strategies, and the overall impact on schools across the USA.
Defining Instructional Coaching
An instructional coach is a trained professional who collaborates with teachers to enhance their instructional practices through mentoring, professional development, and data-driven assessments. Unlike traditional coaches in sports, instructional coaches work behind the scenes, focusing on improving classroom instruction rather than direct student engagement. This role can vary widely between school districts and educators, depending on the specific needs and goals of the educational institution.
The Evolution of Instructional Coaching
Instructional coaching has evolved significantly over the past few decades. The concept gained traction in the late 20th century as schools began recognizing the importance of professional development tailored to individual teacher needs. Today, instructional coaching is often integrated within professional learning communities (PLCs) to foster collaboration and continuous growth among educators.
Key Responsibilities of Instructional Coaches

Instructional coaches have a variety of responsibilities that can be categorized into several key areas:
1. Collaborative Planning
Coaches assist teachers in planning effective lessons tailored to meet the diverse needs of their students. This includes using data to identify student strengths and weaknesses and developing strategies to address these gaps.

2. Classroom Observations
By observing classroom instruction, coaches provide teachers with constructive feedback. This feedback focuses on specific teaching strategies, classroom management techniques, and student engagement methods.
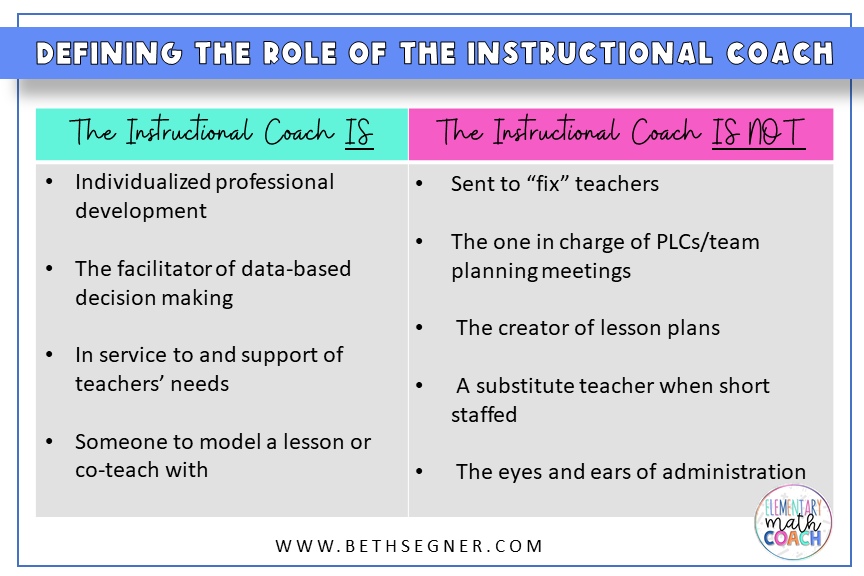
3. Professional Development
Coaches design and facilitate workshops and training sessions that align with the school’s goals and the teachers’ needs. This may include introducing new curricula, teaching technologies, or pedagogical approaches.

4. Data Analysis
Coaches analyze student performance data to identify trends and areas for improvement. This analysis plays a critical role in informing instructional decisions and tailoring support for teachers.

5. Building Relationships
Trust is essential in the coaching relationship. Instructional coaches spend time building rapport with teachers, fostering an environment where educators feel comfortable seeking guidance and sharing challenges.

Benefits of Instructional Coaching
The presence of an instructional coach can bring numerous benefits to schools, teachers, and students alike. Here are some key advantages:

Enhanced Teacher Effectiveness
Instructional coaches provide personalized support to teachers, helping them hone their skills and adapt their teaching practices based on student needs. Research indicates that effective coaching can lead to improved teacher performance, which, in turn, supports student learning.
Improved Student Outcomes
As instructional coaches work with teachers to refine their practices, students often experience enhanced learning outcomes. Schools that implement structured coaching programs have reported higher academic achievement and improved student engagement.
Fostering a Culture of Collaboration
Instructional coaching promotes collaboration among educators, fostering a culture of collective growth and accountability. Teachers working together can share ideas and resources, creating a supportive professional community.
Comparison of Instructional Coaching Models
| Model | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peer Coaching | Teachers collaborate and support each other in instructional practices. | Fosters camaraderie, less hierarchical. | May lack structure and expert guidance. |
| External Coaching | Coaches brought in from outside the district or school. | Fresh perspectives, expertise in specific areas. | Less familiarity with school culture. |
| Instructional Leadership Model | School leaders, such as principals, take on coaching roles. | Strong alignment with school vision. | Leaders may lack coaching training. |
| Content-Specific Coaching | Coaches specialize in a specific subject or grade level. | Expertise in subject matter, tailored support. | May overlook broader teaching strategies. |
Challenges Faced by Instructional Coaches
While the benefits of instructional coaching are substantial, coaches often encounter several challenges that can impede their effectiveness:
Lack of Time
Coaches often juggle multiple responsibilities, which can limit the time available for meaningful interactions with teachers. Schools must prioritize coaching time in their schedules.
Resistance to Change
Some educators may be resistant to feedback or hesitant to change their teaching practices. Coaches must be skilled in fostering a positive, non-threatening environment to encourage openness.
Varying Levels of Readiness
Teachers come with diverse backgrounds and readiness levels. Instructional coaches must differentiate their approaches to meet individual teacher needs effectively.
Effective Strategies for Instructional Coaches
To navigate the complexities of the coaching role successfully, instructional coaches can employ several effective strategies:
Building Relationships
Establishing trust and rapport with teachers is foundational. Coaches should invest time in getting to know educators and understanding their teaching styles and challenges.
Goal Setting
Working collaboratively with teachers to set specific, measurable goals ensures that coaching efforts are focused and intentional. Coaches should regularly revisit these goals to assess progress.
Modeling Practices
Demonstrating effective instructional strategies in the classroom can provide teachers with concrete examples and practical insights they can implement in their own practices.
Providing Ongoing Support
Continuous follow-up and support are crucial in fostering sustained teacher development. Coaches should schedule regular check-ins to discuss progress and challenges.
Instructional Coaching and Technology
In the age of technology, instructional coaches are increasingly integrating digital tools into their practices to enhance teaching and learning. Here are some key areas of focus:
Utilizing Data Tools
Technologies such as learning management systems (LMS) and data analytics platforms can provide valuable insights into student performance. Coaches can help teachers leverage this data to inform instructional decisions.
Facilitating Online Professional Development
With the rise of virtual learning, coaches can lead online workshops and webinars, allowing educators from different locations to collaborate and learn from one another.
Incorporating Educational Technology
Instructional coaches can guide teachers in integrating educational technology into their classrooms, enhancing student engagement and promoting interactive learning experiences.
Real-Life Examples of Successful Instructional Coaching
Let’s look at a few case studies from various schools across the USA that exemplify effective instructional coaching:
Case Study 1: Lincoln High School, California
At Lincoln High, the introduction of an instructional coaching program has led to a significant increase in student engagement and academic performance. Coaches worked closely with teachers using data to inform instructional strategies, resulting in a 20% increase in student test scores over two years.
Case Study 2: Oakwood Elementary, Texas
Oakwood Elementary implemented a content-specific coaching model where coaches focused on literacy. This approach not only improved teacher effectiveness but also reduced the achievement gap among students from diverse backgrounds.
How to Become an Instructional Coach
If you are considering a career as an instructional coach, here are some steps to guide you on your journey:
1. Obtain Relevant Education
Most instructional coaches have a background in education, typically holding a bachelor’s degree in teaching or a related field, followed by a master’s degree in education leadership or curriculum development.
2. Gain Teaching Experience
Before transitioning to coaching, it is essential to gain substantial classroom experience. This experience provides valuable insights into the challenges teachers face and the dynamics of classroom environments.
3. Pursue Professional Development
Continuous professional development is crucial. Attend workshops, conferences, and courses focused on instructional coaching, leadership, and the latest educational trends to enhance your skills.
4. Gain Certification
Some states and institutions offer certifications for instructional coaches, providing additional credentials and demonstrating expertise in the field.
Conclusion
Instructional coaching plays a critical role in fostering a supportive and effective teaching environment. By partnering with educators, instructional coaches help enhance instructional practices, improve student outcomes, and cultivate a culture of collaborative learning. As education continues to evolve, the impact of instructional coaching remains a cornerstone in building better schools for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What qualifications are needed to become an instructional coach?
Typically, an instructional coach should have a background in education, often holding a master’s degree and having teaching experience. Certifications in instructional coaching can enhance qualifications.
How does instructional coaching differ from traditional mentoring?
While both provide support, instructional coaching is usually more structured and focused on improving instructional practices through data-driven feedback, whereas mentoring may focus more on general guidance and support.
What is the role of data in instructional coaching?
Data helps instructional coaches identify areas of need, tailor support for teachers, and track progress in student learning, ensuring that coaching efforts are effective and targeted.
Can instructional coaching lead to improved student performance?
Yes, numerous studies indicate that effective instructional coaching is linked to improved teacher effectiveness, which ultimately leads to enhanced student learning outcomes.
How can schools implement an instructional coaching program?
Schools can start by identifying the needs of their educators, hiring skilled coaches, providing professional development, and ensuring time in the schedule for coaching activities.